AI Restores Faded Art Colors
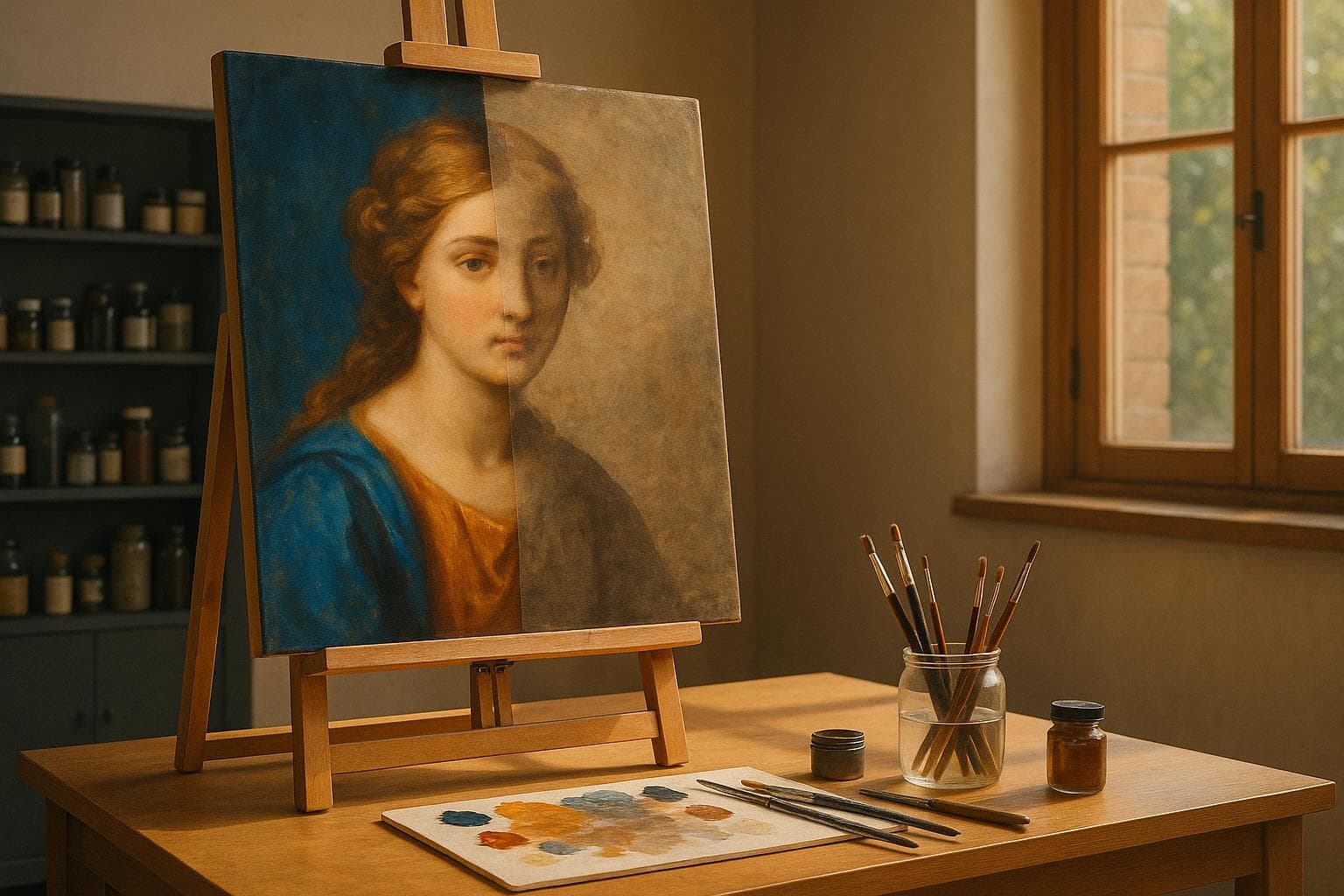

AI Restores Faded Art Colors
AI is transforming art restoration by bringing back the original colors of faded masterpieces. Using advanced imaging and machine learning, AI analyzes pigment traces and reconstructs lost hues with precision. Here's how it works:
- Advanced Imaging: AI uses multispectral and hyperspectral scanning to detect hidden pigment traces invisible to the human eye.
- Machine Learning Models: Tools like CNNs and GANs predict original colors by studying patterns in pigment degradation and artist techniques.
- Historical Data: AI cross-references old photos, artist notes, and chemical analyses to ensure accuracy.
- Real Examples: Projects like restoring Munch's The Scream and recreating Van Gogh’s lost works showcase AI's capabilities.
AI doesn't replace human expertise but enhances it, making art restoration faster, more accurate, and accessible to wider audiences.
How AI Brings Back Faded Art Colors
AI color restoration merges cutting-edge technology with artistic insights to breathe life back into historical artworks. By leveraging advanced imaging techniques and sophisticated algorithms, AI meticulously analyzes and reconstructs the original colors lost to time, bringing these masterpieces closer to their authentic state.
Scanning Artwork with Advanced Imaging
The process begins with high-tech imaging tools that go beyond the capabilities of traditional cameras. Using multispectral and hyperspectral imaging, AI systems scan artworks across various wavelengths of light. This method uncovers hidden pigment traces and creates intricate maps of the artwork's layers, revealing details invisible to the naked eye.
"AI allows us to develop reflectance models, even in a virtual environment", says Pavel Rojtberg, Team Leader at Fraunhofer IGD.
These imaging techniques help pinpoint areas where pigments have faded, track the degradation process, and unearth remnants of the original colors beneath the surface. With this detailed data, AI algorithms take the next step: reconstructing the lost hues with remarkable precision.
Rebuilding Colors with Computer Networks
Once the artwork is scanned, AI systems - powered by convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs) - step in to restore the colors. These neural networks, trained on high-resolution images of artworks from the same era, analyze patterns of pigment wear and the relationships between colors, textures, and brushstrokes. This allows AI to predict the original hues with impressive accuracy.
A standout example is the work of Oxia Palus, which used AI to recreate Van Gogh’s lost painting "Two Wrestlers" from an X-ray image. By training their neural network on Van Gogh’s other works, they were able to restore the painting’s colors and style, capturing the essence of the artist’s technique.
AI also excels at inpainting - filling in missing sections of artwork. For instance, in the restoration of Rembrandt’s "The Night Watch", AI utilized data from copies, X-rays, and digital scans to reconstruct the painting. The restored version is now on display at the Rijksmuseum, showcasing how AI can seamlessly integrate historical and technical data.
Using Historical Records for Accurate Colors
To ensure the restored colors align with the artist’s intent, AI relies heavily on historical documentation and chemical analysis. By examining old photographs, artist notes, and pigment properties, AI determines the materials and techniques originally used in the artwork.
"By using tools and algorithms that process extensive historical data, artificial intelligence has made tremendous progress in researching and replicating past art techniques. AI can 'learn' from unique characteristics and imitate lost processes, allowing us to restore and recreate artistic methods that might have vanished over time", explains Areej Shaikh, Business Content Writer & Strategist.
AI cross-references the chemical properties of historical pigments with traces found in the artwork, ensuring the reconstructed colors aren’t just visually accurate but also true to the original materials and methods. Historical records also provide crucial context about artistic movements and stylistic choices, guiding AI when reconstructing ambiguous or missing areas.
This meticulous approach has yielded impressive results. AI systems can now distinguish between authentic works and reproductions with over 90% accuracy. One notable initiative is the PERCEIVE project, funded by the European Union, which brings together 12 major institutions to create AI tools for color restoration across various mediums, including paintings, textiles, and photographs.
Real Examples of AI Art Restoration Success
Projects around the world are demonstrating how AI can breathe new life into historical art by bringing back faded colors. These examples showcase how technology is helping to preserve and revive the original vibrancy of diverse art forms.
Restoring Edvard Munch's The Scream
The MUNCH Museum in Oslo, Norway, is at the forefront of an ambitious project to digitally restore the original colors of Edvard Munch's The Scream. As part of the EU-supported PERCEIVE initiative, the museum has developed an interactive tool called "The Scream Time Machine." This program allows users to see how the painting may have looked in 1893 and how it might change in the future due to environmental factors.
Irina Crina Anca Sandu, a conservation scientist at the museum and the lead researcher on the project, explains the importance of context in their work:
"It's always important that, when I make an interpretation of this data, I bring in the context... The first context for The Scream, in this case, is what Munch writes: how he got inspired from nature, from these colors of the sunsets".
Using AI, the team digitally reconstructs the artwork to counteract damage caused by light, humidity, and handling - without altering the physical painting itself. Early versions of these AI tools were unveiled at the 6th annual International Conference on Innovation in Art Research and Technology, held in Oslo in June 2024.
Reviving Song Dynasty Silk Paintings
Ancient Chinese silk paintings, known for their intricate details and delicate materials, pose unique restoration challenges. AI systems are stepping in to analyze these artworks by studying brush strokes, color palettes, and material compositions. By comparing this data to authenticated pieces from the same era, AI can identify patterns of aging, such as oxidation and chemical changes, and distinguish them from actual damage.
These AI models are trained to understand the techniques of Song Dynasty artists, enabling them to reconstruct faded pigments with impressive precision. This approach not only restores the paintings' original vibrancy but also preserves the essence of the artists' craftsmanship.
Restoring Pre-Columbian Frescoes
AI is also making strides in preserving ancient American wall paintings, offering valuable insights into pre-Columbian civilizations. For example, AI-powered tools have recently identified 303 new Nazca geoglyphs in just six months - a task that previously took nearly a century to accomplish. The same pattern recognition technology is being used to restore frescoes, helping researchers uncover original color schemes and artistic methods.
At archaeological sites like Mayapan and Calakmul in Mexico, AI is combined with advanced conservation techniques. At Calakmul, researchers used calcium hydroxide nanoparticles to address issues like water infiltration and salt damage. This method not only stabilized the wall paintings but also reformed the pigment binders, preserving the authentic colors of the original artwork.
These examples highlight how AI is transforming art restoration, offering new ways to preserve and celebrate cultural heritage.
Ethics and Culture in AI Restoration
AI's role in reviving lost colors and details in art restoration is undeniably groundbreaking, but its application must tread carefully to honor artistic intent and cultural heritage. While these technologies open new doors for preserving and sharing art, they also spark essential conversations about authenticity and heritage. Navigating this intersection requires balancing technological advancements with respect for the original work and the cultural context it represents. These ethical considerations are crucial as we explore how AI can expand public access to art and its history.
Balancing Restoration and Original Art
One of the toughest challenges in AI-driven restoration lies in respecting the artist's original vision while addressing the inevitable wear and tear that comes with time. This is where human expertise becomes indispensable, guiding technology to ensure the essence of the artwork remains intact.
Julian Baumgartner, a seasoned art conservator, highlights this point:
"Conservation is still a craft. Despite all of the scientific advances, the practitioner still needs to have the technical ability".
AI isn't here to replace human skill but to complement it. For instance, an AI system achieved over 90% accuracy in identifying authentic Rembrandt pieces versus forgeries, showcasing its potential as a powerful tool in art conservation.
The Metropolitan Museum of Art captures the essence of this collaborative approach:
"the evolution of a sensibility that respects the artist's original intent and the materials used".
This underscores the importance of maintaining artistic integrity while leveraging technology. But restoration isn’t just about the art itself - it’s also about connecting the public to these efforts and the stories behind them.
Public Access to Restoration Projects
AI-powered restoration is reshaping how people engage with art, making the process more transparent and educational. Museums are now using augmented reality to offer visitors a side-by-side look at artworks before and after restoration. This real-time insight into the restoration process not only educates but also deepens appreciation for the effort behind preserving cultural treasures. AI even customizes these learning experiences for different audiences, from young students to seasoned art historians, helping everyone connect on their level.
Beyond museum walls, AI platforms have reached over 4 million learners worldwide, proving how scalable and impactful these technologies can be. Virtual reconstructions of historical sites, once out of reach, are now bringing history to life in immersive and interactive ways. For example, researchers at the University of Rome La Sapienza are using AI to analyze the Colosseum's facade, pinpointing cracks and erosion to guide precise restoration efforts. These findings are shared globally, enabling faster and more effective conservation work.
AI also plays a crucial role in training the next generation of conservators. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) simulations, coupled with 3D scanning and printing, allow students to practice restoration techniques without risking damage to original pieces. Such tools make the field more accessible and hands-on for learners worldwide.
As Team DigitalDefynd aptly puts it:
"Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into the realm of art restoration and preservation marks a transformative shift in how we approach the safeguarding of cultural heritage".
sbb-itb-e44833b
How Platforms Like Museumfy Improve Art Experiences
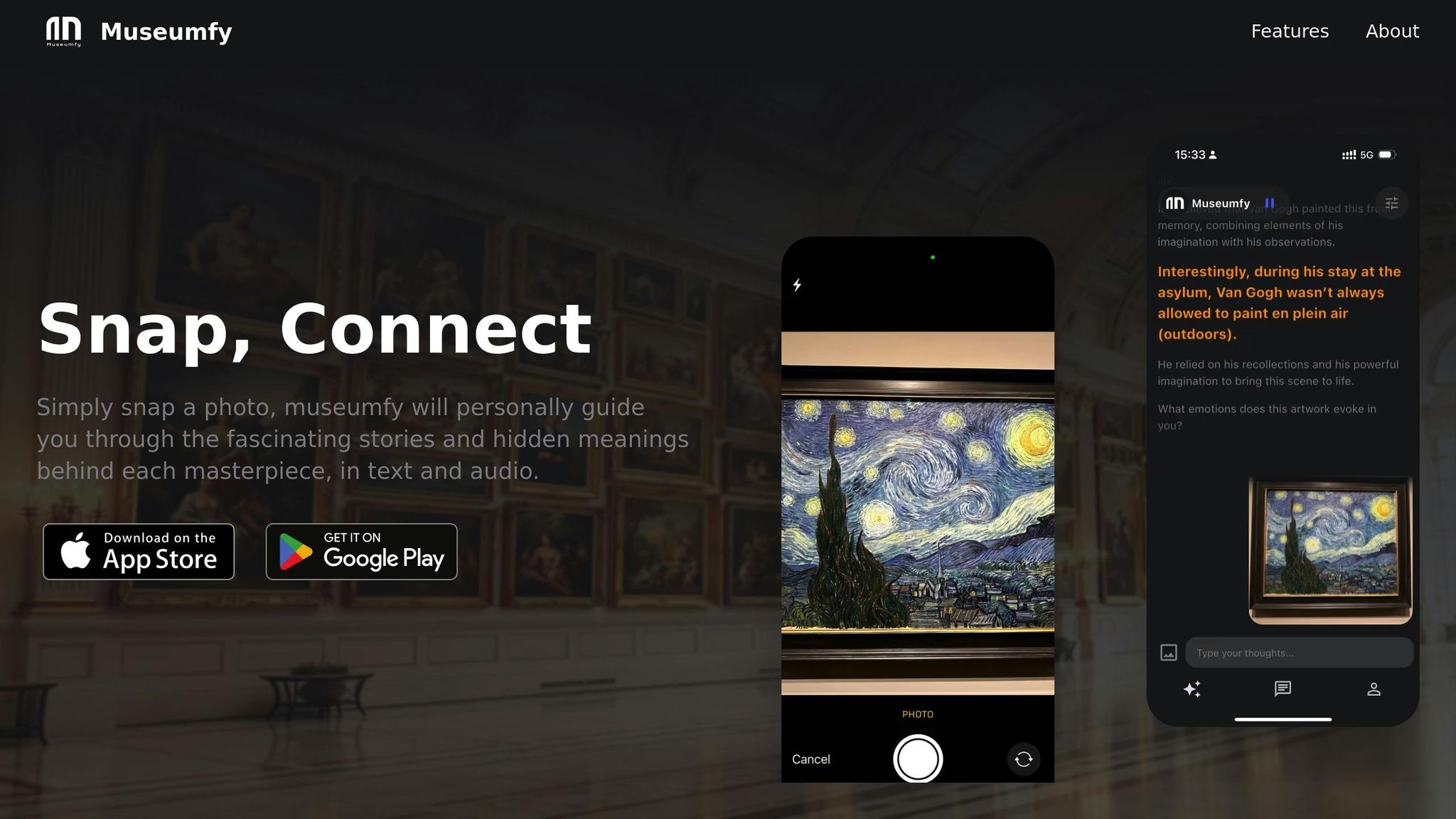
Platforms like Museumfy are reshaping the way people engage with art, blending advanced AI-driven restoration techniques with user-friendly tools. By making the science of art restoration accessible to the public, Museumfy bridges the gap between the intricate processes behind restoring masterpieces and the stories that make these works meaningful. This approach not only enhances appreciation but also deepens connections with the rich histories of these artworks.
Personal Learning Through AI
Museumfy has taken art education to a new level, using AI to provide personalized insights about restored works of art. With just a snap of a photo, users can instantly learn about the creation and restoration of a masterpiece.
The platform boasts an impressive 90% accuracy rate and supports over 20 languages. This means that whether you're a Spanish speaker marveling at the restored vibrancy of a Renaissance fresco or a Japanese tourist exploring the same piece, you'll receive the same detailed explanations in your native language. The platform adapts its content based on the user - offering technical details for students and art enthusiasts, while presenting engaging narratives for casual viewers.
Museumfy uses the same advanced AI technology employed in imaging and color reconstruction to make the science of restoration understandable. For example, instead of simply noting that a painting’s colors were revived, Museumfy explains the significance of specific pigments to the original artist and how their restoration shifts our perception of the piece. Users can choose between detailed text explanations or audio guides, making the platform accessible to those who prefer to read or listen.
"AI's capabilities extend from predictive degradation analysis and meticulous restoration guidance to automating environmental controls and archival processes. This technology improves the precision and effectiveness of conservation efforts and democratizes access to sophisticated restoration techniques, fostering global collaboration and knowledge sharing".
This tailored approach not only makes restoration science more engaging but also opens the door for a wider audience to appreciate the intricate work that goes into preserving art.
Making Art Available to Everyone
Museumfy is also breaking down financial barriers to art education. While traditional audio guides at museums can cost $15–$25 per visit, Museumfy’s Premium Plan provides unlimited insights for just $9.99 per month. For those on a budget, the Free Plan allows users to access up to five photo insights each month, ensuring that cultural education remains accessible to all.
Beyond affordability, Museumfy’s inclusive design ensures that people from different backgrounds can connect with restored art in a way that feels relevant to them. By offering insights tailored to various languages and perspectives, the platform makes it easier for international visitors to engage with the stories behind the art.
Research highlights the role of AI tools in sparking public interest in art conservation, helping to build awareness and support for preservation efforts. When people learn how AI has been used to restore the original colors of ancient frescoes or uncover hidden layers in famous paintings, they gain a deeper appreciation for both the artworks and the efforts to protect them. This awareness often translates into greater advocacy and funding for future restoration projects.
For educational institutions and tour groups, Museumfy’s Enterprise Plan offers custom integrations tailored to specific curricula or cultural programs. This means that a high school art class in Ohio can access the same cutting-edge insights about restored masterpieces as graduate students at top art schools. By leveling the playing field, Museumfy is making art education more equitable and impactful than ever before.
Conclusion: Preserving History with AI
AI is transforming the world of art restoration, breathing new life into faded masterpieces and uncovering hidden layers of history. By accurately detecting faded hues, filling in missing details, and reconstructing original colors, AI goes beyond surface-level restoration. It digs deeper, unveiling insights buried under centuries of wear and neglect.
Take, for instance, the digital reconstructions of Gustav Klimt’s lost paintings from World War II. By analyzing his existing works, AI has recreated these lost treasures, preserving their essence for future generations. This blend of technology and artistry doesn’t just restore the physical appearance of art - it safeguards its cultural and historical significance.
AI achieves this level of precision by combining historical records with chemical analysis, ensuring that the restoration process respects the artist's original vision while addressing the toll of time. But the impact of AI isn’t limited to individual artworks. Researchers are also applying AI to analyze damage patterns in historical sites, enabling focused preservation efforts and protecting larger cultural landmarks.
Beyond restoration, AI is also making art more accessible. Advanced platforms are transforming complex restoration processes into engaging experiences for the public. Joan Kee, the Judy and Michael Steinhardt Director of the Institute of Fine Arts at NYU, emphasizes the complementary role of AI in art:
"AI can provide valuable insights in the analysis of art, but it should be viewed as a tool rather than a replacement for human expertise".
Platforms like Museumfy exemplify this collaborative approach, combining AI-driven restoration with expert curation to create interactive, personalized experiences. Thanks to tools like these, a student in rural Ohio can explore the same detailed narratives about restored Renaissance frescoes as someone visiting a world-renowned museum. With a 90% accuracy rate and support for over 20 languages, Museumfy ensures that these stories are accessible to anyone with a smartphone and a curiosity for history.
Looking ahead, AI’s role in art restoration will only become more advanced. While today it helps recover faded pigments and recreate lost works, tomorrow it could power immersive virtual experiences that bring ancient masterpieces to life in entirely new ways. The challenge lies in maintaining a careful balance - leveraging technology while staying true to the authenticity of the original artwork. By doing so, we can preserve the creative genius of the past while embracing the possibilities of the future.
So, the next time you admire a restored painting or visit a museum, take a moment to appreciate the incredible partnership between human skill and artificial intelligence. Snap a photo, dive into the story behind the artwork, and marvel at how AI is helping to preserve art’s rich history - one brushstroke at a time.
FAQs
How does AI tell the difference between faded colors and actual damage in artwork?
AI leverages machine learning to scrutinize high-resolution scans of artworks, comparing them against historical records or similar pieces. By analyzing details like color patterns, texture, and structural elements, it can differentiate between pigment fading and physical damage. For instance, AI can pick up on slight color shifts that signal fading, separating them from cracks or other structural imperfections.
This capability empowers conservators to make informed restoration choices. By mapping the artwork's current state and even simulating its original colors, AI ensures that repairs honor the piece's authenticity while reviving its original vibrancy.
How do historical records help AI restore the original colors of faded artwork?
Historical records are crucial for enabling AI to restore the original colors of faded artwork with precision. These records detail the materials, pigments, and techniques that artists used, giving AI a solid base to work from.
With this information, AI can analyze and make educated choices to recreate colors that are both visually striking and true to the artwork's historical context. This approach ensures that the restoration honors the artist's vision while maintaining the piece's historical and cultural importance.
How does AI make art restoration projects more accessible and engaging for the public?
AI is reshaping the way people connect with art restoration, making it more approachable, interactive, and engaging. Take AI-powered tools, for instance - they can digitally revive faded artwork, giving viewers a glimpse of how these pieces might have looked when first created. Pair this with augmented reality (AR), and museum visitors can explore restored versions of historic artifacts through interactive apps or displays, creating a deeper connection to the art.
On top of that, AI fosters global collaboration among art restoration experts. By linking professionals from different corners of the world, it ensures a variety of perspectives contribute to the conservation process. This exchange of ideas not only enhances the restoration itself but also enriches how the public values and understands cultural heritage. These technologies are bridging the gap between art restoration and the audience, making the experience both educational and enjoyable.